Optimised irrigation systems
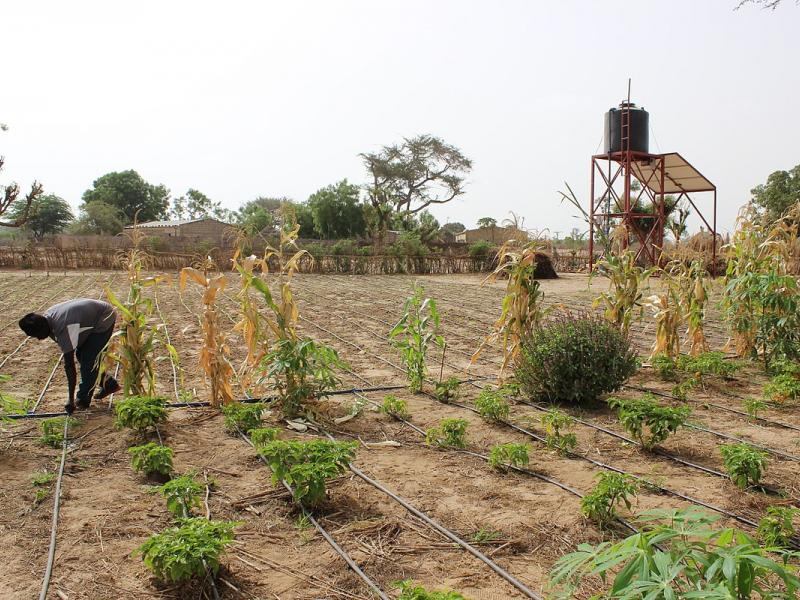

Description of the innovative solution
Agriclulture is the largest user of water among human activities. Water withdrawals for agriculture are estimated to be around 70% of all use of water. Climate change is becoming more prevalent globally with increased incidence of extreme weather events, such as prolonged droughts, combined with increasingly frequent heat waves. To mediate and adapt, it is essention to set up of innovative irrigation water management to ensure fresh water for human consumption and agricultural production as well as to preserve the environment. These optimised irrigation systems will provide an opportunity for...
Agriclulture is the largest user of water among human activities. Water withdrawals for agriculture are estimated to be around 70% of all use of water. Climate change is becoming more prevalent globally with increased incidence of extreme weather events, such as prolonged droughts, combined with increasingly frequent heat waves. To mediate and adapt, it is essention to set up of innovative irrigation water management to ensure fresh water for human consumption and agricultural production as well as to preserve the environment. These optimised irrigation systems will provide an opportunity for reduced water demand in irrigation and ensure food production as climate changes. Different irrigation systems have been put into place or are currently in the pipeline. Drip irrigation is an irrigation system where water drips onto the soil at very low rates (2 - 20 liters/hour) from a system of small diameter plastic pipes fitted with outlets called emitters or drippers. Water is applied close to plants so that only part of the soil in which the roots grow is wetted, unlike surface and sprinkler irrigation, which involves wetting the entire soil profile. In principle, there are two types of drip irrigation: sub-surface drip irrigation - water is applied below the soil surface and surface drip irrigation - Water is applied directly to the soil surface. Automated and smart irrigation system can also optimise the frequency and duration of irrigation.
Examples and additional resources
Real-world examples
See this solution in action in different contexts and settings around the world
Additional resources
Learn more about this solution through studies, articles, business cases, and other information
Optimizing Irrigation for Water Management
Optimised Irrigation System Selection Model
Contacts
Connect to others working on and with this solution around the world
Pathways to uptake
Engage with our “backcasting tool” to imagine and design “pathways to uptake” for this solution in your setting.
This process involves defining a future vision of this solution being used in your context, and then working “backwards” to identify necessary steps to achieve this vision by 2030. Going through this exercise as an individual or with a team can help to clarify the WHAT/WHEN/HOW of moving a solution (or package of solutions) towards having major impact. We hope these pathways will inspire outside-of-the-box thinking, creative approaches, and actionable concrete steps to move ideas into action.
Pathway builder
Explore pathways for this solution
Be the first one and add a pathway for this solution!