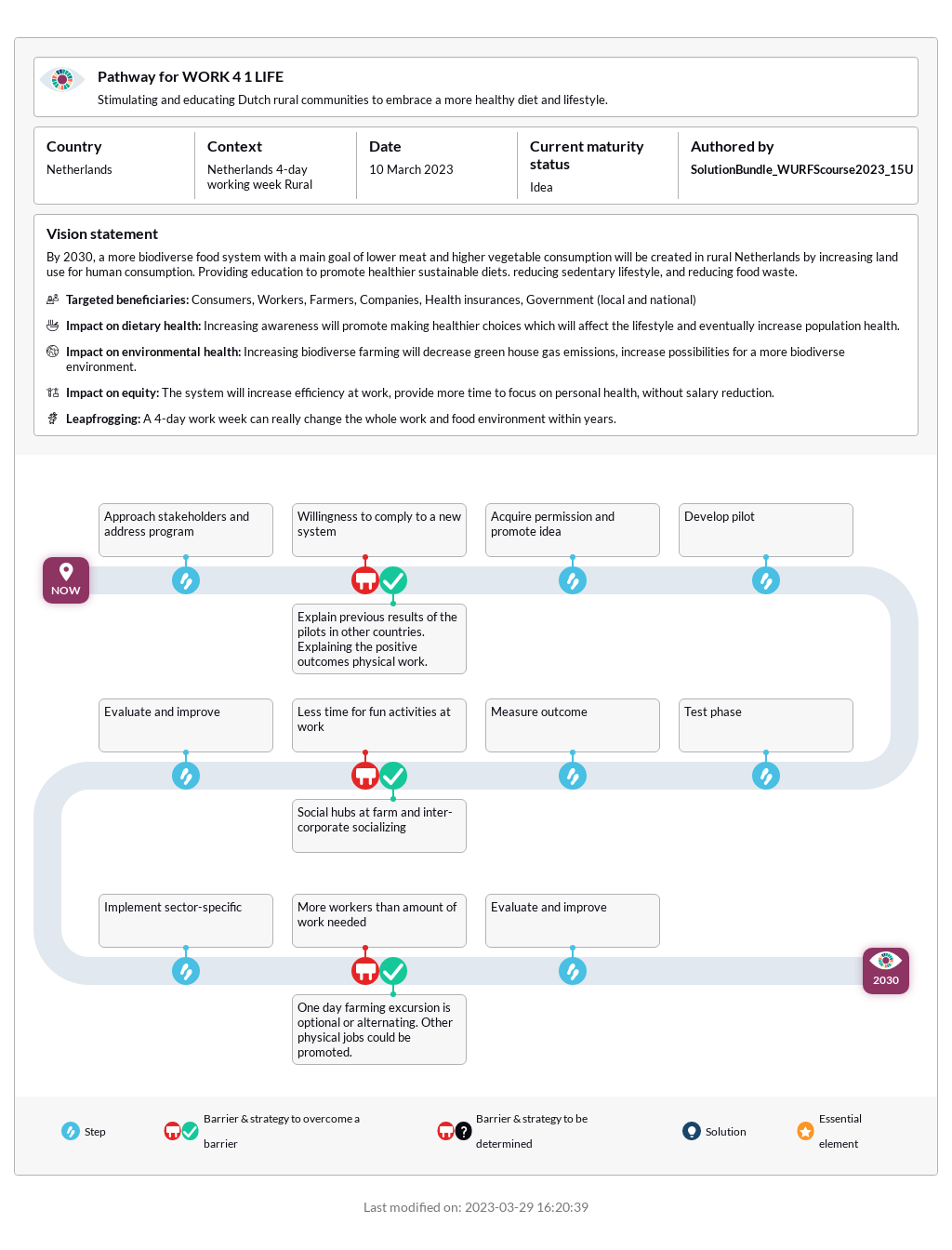
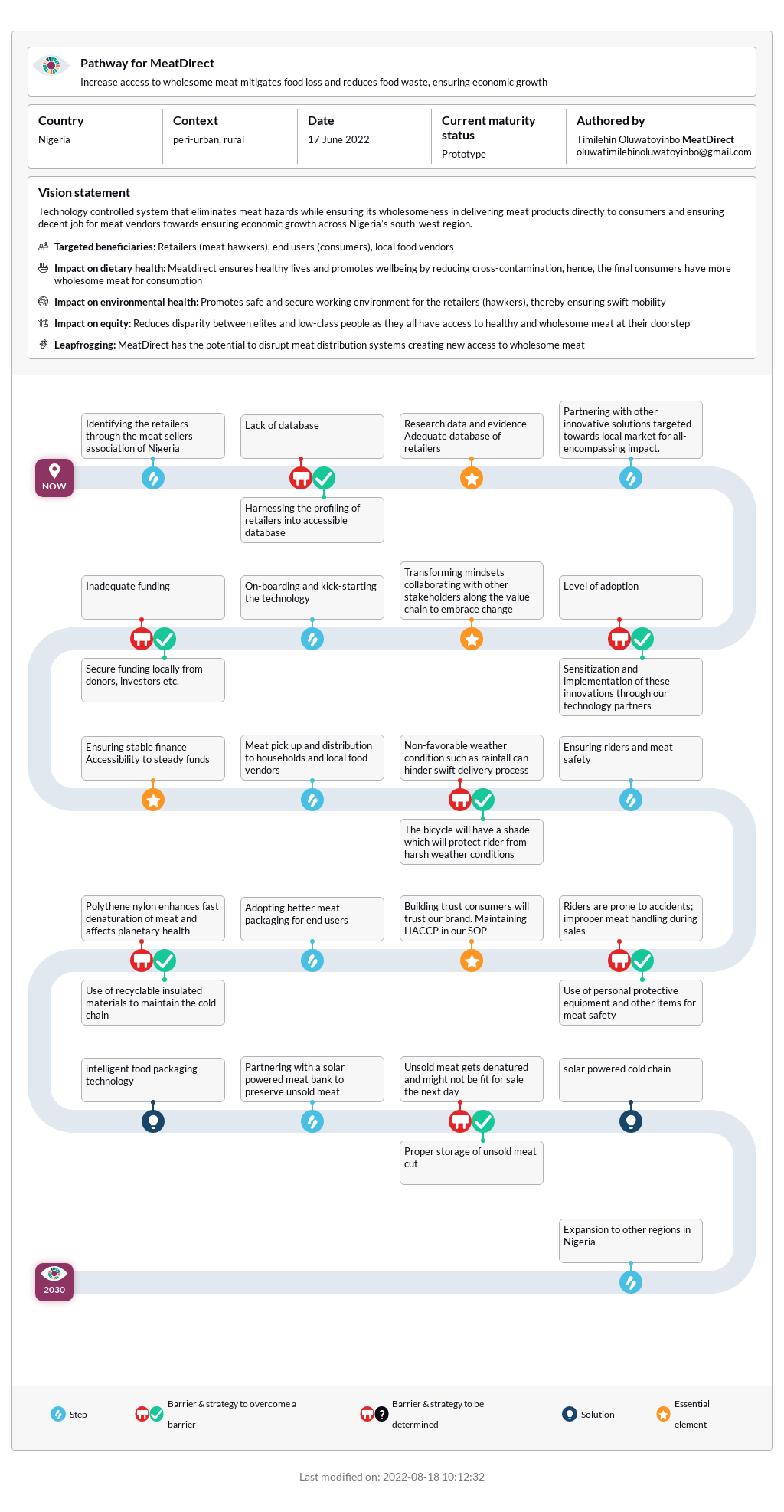
Upcycling is the process of transforming consumer or production waste or byproducts into new materials, often for environmental or artistic reasons. Food loss and waste are urgent issues for hunger reduction. Additionally, they cause negative environmental impacts and are economically costly, for individuals and nations. Upcycled foods proposes to turn food waste along the food chain into new, value-added nutritious products, thereby creating new revenue streams. Diverse businesses exploiting food waste are currently emerging. These range from mayonnaise made with aquafaba, a waste stream from...
Upcycling is the process of transforming consumer or production waste or byproducts into new materials, often for environmental or artistic reasons. Food loss and waste are urgent issues for hunger reduction. Additionally, they cause negative environmental impacts and are economically costly, for individuals and nations. Upcycled foods proposes to turn food waste along the food chain into new, value-added nutritious products, thereby creating new revenue streams. Diverse businesses exploiting food waste are currently emerging. These range from mayonnaise made with aquafaba, a waste stream from the chickpea industry, to cereal bars made of spent grains from the beer industry. Upcycled products can increase businesses’ revenue, decrease global food waste, and create novel, nutrient-dense products. Upcycling can occur on farms and within factories, or byproducts can be distributed to other producers for different uses. For farmers, they waste fewer of their resources, as upcycling allows more of their products to feed people. As companies work to demonstrate their commitment to environmental sustainability, food manufacturers reusing food byproducts underscores their work. When smaller businesses upcycle food that has already been produced, they do not have to grow more food or obtain excess land or water. Likewise, consumers are interested in taking actions that they believe will help the environment, and people purchasing upcycled products may support their mission. Food upcycling companies have sprung up around the world over the last few years, using food waste from other companies, suppliers, and producers, or their own food production, but the process has yet to become a standard practice in global food systems.