Clay pot cooler
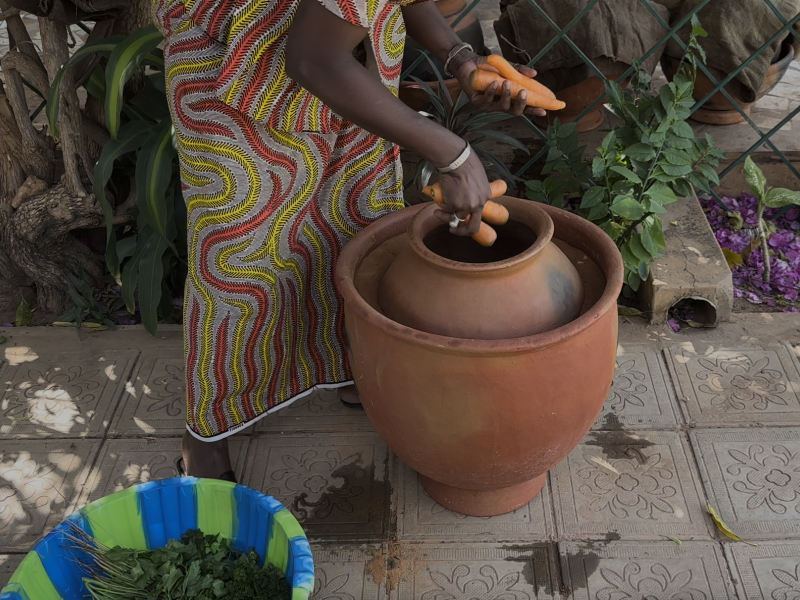
Description of the innovative solution
Clay pot coolers are simple and inexpensive technologies that can be made with locally available materials and do not require electricity to operate. By providing a cool humid environment, clay pot coolers can improve the shelf life of many common fruits and vegetables in dry regions. Clay pot coolers work through the evaporation of water, providing a stable cool and humid environment that is well-suited for storing most fruits and vegetables for longer periods of time. Because clay pot coolers are cooled through the evaporation of water, they work best in hot and dry climates that allow water...
Clay pot coolers are simple and inexpensive technologies that can be made with locally available materials and do not require electricity to operate. By providing a cool humid environment, clay pot coolers can improve the shelf life of many common fruits and vegetables in dry regions. Clay pot coolers work through the evaporation of water, providing a stable cool and humid environment that is well-suited for storing most fruits and vegetables for longer periods of time. Because clay pot coolers are cooled through the evaporation of water, they work best in hot and dry climates that allow water to evaporate. If used properly, clay pot coolers provide many benefits, including reduced food waste, time and money saved, and increased availability and consumption of nutritious fruits and vegetables. There are two primary types of clay pot coolers: clay pot-in-pot and clay pot-in-dish. The clay pot-in-pot design uses an outer clay pot with a large opening that can accommodate the inner pot. This design typically offers better performance. On the other hand, the clay pot-in-dish design utilizes a plastic, metal, or clay dish or basin as the outer vessel. This design is easier to make and utilizes widely available materials. Both designs feature a clay pot as the inner vessel and a jute sack or cloth cover. Overall, clay pot coolers provide a practical and effective solution for preserving fresh produce, particularly in hot and arid climates.
Examples and additional resources
Real-world examples
See this solution in action in different contexts and settings around the world
Technology evaluation in Mali
Technology evaluation in Rwanda/Burkina Faso
Technology evaluation in Rwanda/Burkina Faso
Additional resources
Learn more about this solution through studies, articles, business cases, and other information
Cooling technology evaluation in Mali
Heat and mass transfer model
Assembling, using, and maintaining clay-pot-coolers
6-year project summary report
Training program outcomes and impacts
Clay pot cooler overview video
Agrilinks blog post
Engineering for Change blog post
USAID/Medium blog
Contacts
Pathways to uptake
Engage with our “backcasting tool” to imagine and design “pathways to uptake” for this solution in your setting.
This process involves defining a future vision of this solution being used in your context, and then working “backwards” to identify necessary steps to achieve this vision by 2030. Going through this exercise as an individual or with a team can help to clarify the WHAT/WHEN/HOW of moving a solution (or package of solutions) towards having major impact. We hope these pathways will inspire outside-of-the-box thinking, creative approaches, and actionable concrete steps to move ideas into action.
Pathway builder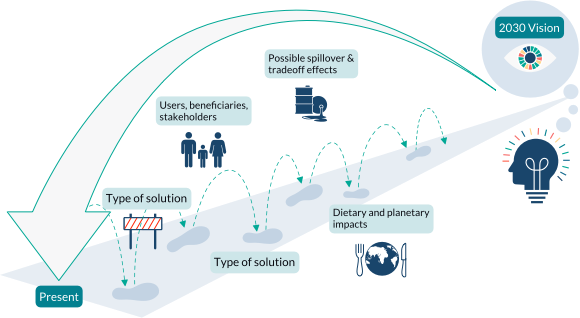
Explore pathways for this solution
Be the first one and add a pathway for this solution!