Aquaponics
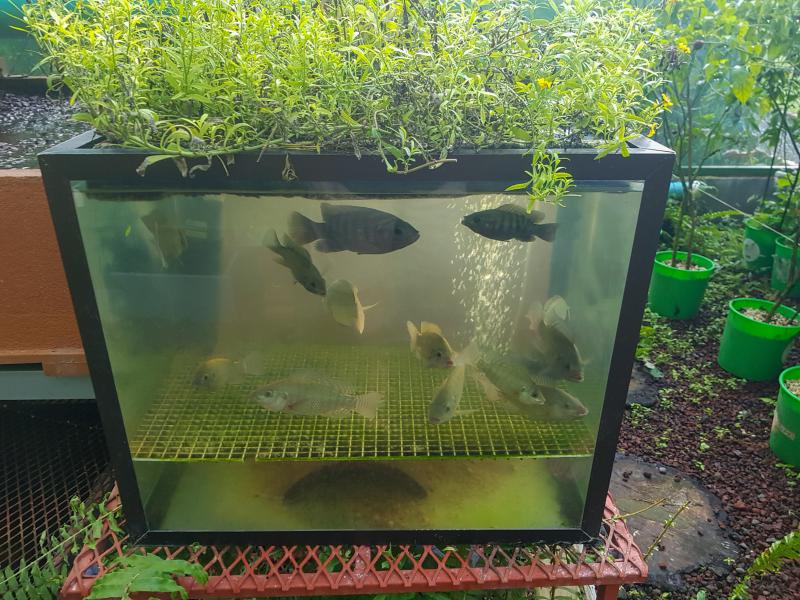

Description of the innovative solution
Countries need to find safe production systems that can provide access to good protein sources. Fish is a nutritious food source, however, in urban settings or landlocked regions availability of fresh fish is often limited. Vertically integrated urban aquaculture systems and floating aquaponic farms are examples of innovations that can address this challenge. Aquaponics combines aquaculture, growing aquatic animals in controlled conditions, and hydroponics, growing plants without soil. The plants and fish are grown in the same tank and have a symbiotic relationship. The vegetables receive...
Countries need to find safe production systems that can provide access to good protein sources. Fish is a nutritious food source, however, in urban settings or landlocked regions availability of fresh fish is often limited. Vertically integrated urban aquaculture systems and floating aquaponic farms are examples of innovations that can address this challenge. Aquaponics combines aquaculture, growing aquatic animals in controlled conditions, and hydroponics, growing plants without soil. The plants and fish are grown in the same tank and have a symbiotic relationship. The vegetables receive nutrients and beneficial bacteria from the fish waste, and the plants clean the water, which cycles back to the fish. The beneficial bacteria from the fish converts the waste into nutrients the plants can use to grow. People can create aquaponic systems in their homes or they can be scaled up to the commercial level. In urban areas with limited fertile soil, aquaponics provides nutrient-dense food to people and uses less water than traditional methods of agriculture. Unused urban spaces that are unfit for other purposes could be used to house vertical urban aquaculture systems. Urban aquaculture systems could also be built in containers. Feed would be processed in situ or nearby. Urban organic market waste or household waste can be used to upcycle into fish feed. Also systems which combine aquaculture (e.g. production of fish) and hydroponics (growing plants in water) is a possible solution. Shrimp Paddy Culture (SPC), is another solution suitable in more rural environments, when facing salt water intrusion. SPC seeks to provide rural opportunities for the agricultural sector to mitigate urban migration and poverty.
Examples and additional resources
Real-world examples
See this solution in action in different contexts and settings around the world
Aquaponics companies around the world
Green Life Aquaponics business
Additional resources
Learn more about this solution through studies, articles, business cases, and other information
Costs and profit margins of aquaponics
Contacts
Connect to others working on and with this solution around the world
Pathways to uptake
Engage with our “backcasting tool” to imagine and design “pathways to uptake” for this solution in your setting.
This process involves defining a future vision of this solution being used in your context, and then working “backwards” to identify necessary steps to achieve this vision by 2030. Going through this exercise as an individual or with a team can help to clarify the WHAT/WHEN/HOW of moving a solution (or package of solutions) towards having major impact. We hope these pathways will inspire outside-of-the-box thinking, creative approaches, and actionable concrete steps to move ideas into action.
Pathway builder
Explore pathways for this solution
Be the first one and add a pathway for this solution!